Oscilloscopes are indispensable test and measurement equipment used to visualise and analyse electrical signals—a task that engineers and technicians often undertake. By providing a graphical representation of voltage waveforms, they help these professionals perform waveform analysis and diagnose circuit behaviour. With several kinds of oscilloscopes available, each with its own unique features and advantages, it is important to know how to select the right one for a specific application.
This guide explores the 4 main types of oscilloscopes, their features, and the scenarios they are most suited for.
1. Analogue Oscilloscopes
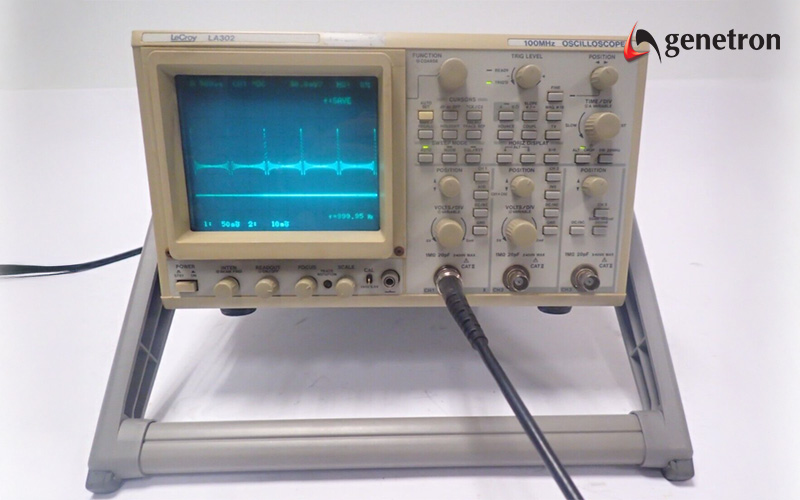

Analogue oscilloscopes have been a staple signal measurement tool for decades. However, they are mostly using outdated technology, which explains their limited speed and waveform analysis capabilities. This particular type of oscilloscope uses electron beams to produce a continuous waveform display on a cathode-ray tube (CRT). It is also worth noting that analogue oscilloscopes have been almost completely phased out.
Key Features:
- Provides real-time visualisation of waveform signals.
- Its simplicity makes it easy to observe signal changes as they occur.
Advantages:
- It is ideal for monitoring simple, repetitive waveforms.
- Low latency since it directly displays signals without digital processing.
Limitations:
- Restricted bandwidth and no capability for signal storage or complex analysis.
- Less suitable for high-bandwidth signal testing or advanced diagnostics.
Best Use Scenarios:
Analogue oscilloscopes are excellent for basic signal monitoring and applications where real-time feedback on simple waveforms is sufficient.
2. Digital Oscilloscopes
Digital oscilloscopes have revolutionised waveform analysis by converting analogue signals into a digital format for precise measurement, advanced analysis capabilities, storage, and compatibility with third-party apps such as Matlab, Excel, and Labview. They are now the go-to choice for most modern applications.
Key Features:
- Converts and processes signals digitally for enhanced accuracy.
- Offers advanced features like signal storage, automatic measurements, and advanced triggering.
Advantages:
- Enables detailed analysis of transient events and non-repetitive signals.
- Provides options for zooming in on sections of waveforms for closer examination.
Limitations:
- More expensive than analogue counterparts.
- Requires some training to handle its advanced features effectively.
Best Use Scenarios:
These types of oscilloscopes are perfect for applications demanding high accuracy, detailed diagnostics, and complex waveform analysis. They are widely used in research and development, manufacturing, and electronics repair.
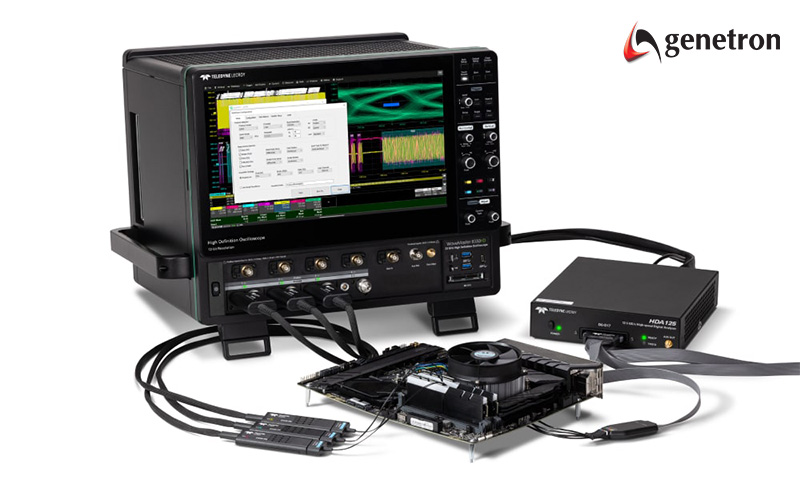
3. Mixed-Signal Oscilloscopes (MSO)
Mixed-signal oscilloscopes (MSOs) combine the capabilities of digital and analogue oscilloscopes, enabling simultaneous analysis of analogue and digital signals. This versatility makes them invaluable for testing systems with integrated digital and analogue components.
Key Features:
- Analyses both digital and analogue signals side by side.
- Provides tools for decoding communication protocols such as I²C and SPI.
Advantages:
- Simplifies testing of embedded systems, reducing the need for multiple instruments.
- Effective for troubleshooting circuits that combine analogue and digital components.
- Utilises digital channels (usually 16 or more) to capture digital signals, freeing up analogue channels (usually 4) to capture voltage over time signals.
Limitations:
- Can be costlier than standard digital oscilloscopes.
- Fewer channels than a dedicated logic analyser
Best Use Scenarios:
MSOs are the ideal type of oscilloscope for testing microcontrollers, embedded systems, and complex electronic devices that rely on mixed-signal environments.
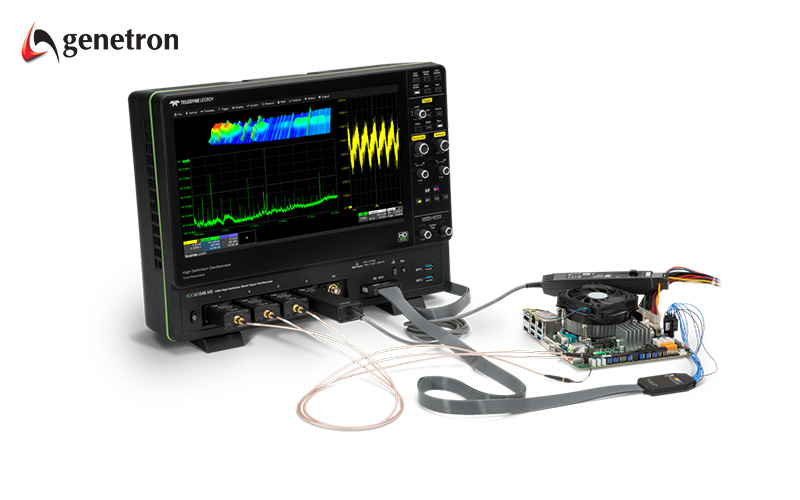
4. High-Speed Oscilloscopes
High-speed oscilloscopes are engineered for high-frequency applications where rapid and precise waveform analysis is required. With superior sample rates and bandwidth, they excel in environments where signals change rapidly.
Key Features:
- High sample rates and bandwidths, suitable for high-bandwidth signal testing.
- Advanced data acquisition and processing capabilities.
Advantages:
- Provides unparalleled detail for fast-changing or high-frequency signals.
- Essential for cutting-edge applications in telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive industries.
Limitations:
- Often more expensive due to their advanced capabilities.
- Larger and more complex compared to standard oscilloscopes.
Best Use Scenarios:
High-speed oscilloscopes are indispensable in fields like 5G technology development, radar testing, and automotive electronics, where precision and speed are crucial to operations.
Choosing the Right Oscilloscope
Selecting the most suitable type of oscilloscope depends on the nature of the application, and if there are specific requirements:
- Frequency/Bandwidth: Determine the highest frequency of the signals you need to measure. As a rule of thumb, the oscilloscope’s bandwidth should be at least 3–5 times the signal’s highest frequency.
- Sampling Rate: Look for a rate of at least 4–10 times the bandwidth for accurate signal representation.
- Channel Count: Decide how many signals you need to measure simultaneously (2, 4, or more channels).
- Memory Depth: A deeper memory allows for capturing longer waveforms or higher sampling rates.
Understanding what is needed for different scenarios can help you select the best test and measurement equipment to optimise your results and streamline your workflow.
Oscilloscopes play a critical role in signal measurement and waveform analysis, with each type catering to specific requirements. Whether you are working on simple circuits or advanced embedded systems, having the right oscilloscope can significantly enhance your testing capabilities.
Here at Genetron Singapore, we offer a complete selection range of oscilloscopes, from basic teaching lab-based oscilloscopes, to cutting-edge high-speed oscilloscopes that can handle the rigours of rapid signal testing in a 5G world. Boasting a bandwidth of up to 65 GHz, 12-bit resolution, and a sampling rate of 320 GS/s, our high-speed oscilloscopes are capable of delivering exceptional accuracy for a wide range of advanced applications, such as DDR memory testing.
For more information about our products, please contact us today.